USMLE-STEP-3 Online Practice Questions and Answers
A 68-year-old White male, with a history of hypertension, an 80 pack-year history of tobacco use and emphysema, is brought into the ER because of 4 days of progressive confusion and lethargy. His wife notes that he takes amlodipine for his hypertension. He does not use over-the-counter (OTC) medications, alcohol, or drugs. Furthermore, she indicates that he has unintentionally lost approximately 30 lbs in the last 6 months. His physical examination shows that he is afebrile with a blood pressure of 142/85, heart rate of 92 (no orthostatic changes), and a room-air O2 saturation of 91%. He is 70 kg. The patient appears cachectic. He is arousable but lethargic and unable to follow any commands. His mucous membranes are moist, heart rate regular without murmurs or a S3/S4 gallop, and extremities without any edema. His pulmonary examination shows mildly diminished breath sounds in the right lower lobe with wheezing bilaterally. The patient is unable to follow commands during neurologic examination but moves all his extremities spontaneously. Laboratory results are as follows:
Blood Sodium: 109 Potassium: 3.8 Chloride: 103 CO2: 33 BUN: 17 Creatinine: 1.1 Glucose: 95 Urine osmolality: 600 Plasma osmolality: 229 White blood cell (WBC): 8000 Hgb: 15.8 Hematocrit (HCT): 45.3 Platelets: 410 Arterial blood gas: pH 7.36/pCO2 60/pO2 285 A chest x-ray (CXR) reveals a large right hilar mass.
What is the most likely cause of this patient's altered mental status?
A. sepsis syndrome with pneumonia
B. ischemic stroke
C. central pontine myelinolysis
D. cerebral edema
E. respiratory acidosis
A 53-year-old fisherman develops pain and swelling of the right hand 8 hours after suffering a fish hook injury to the finger. On physical examination, the patient's temperature is 102.8°F and the patient ap pears septic. The patient's hand and a Gram stain of material aspirated from a bulla are shown in Figures below.
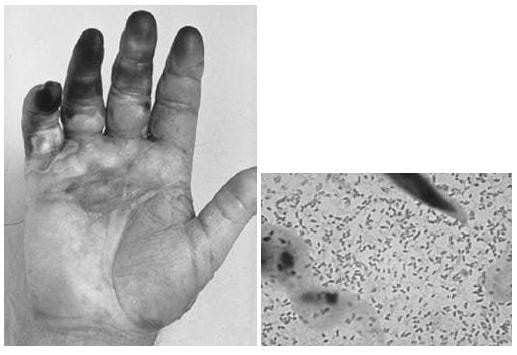
After appropriate wound care and debridement of necrotic tissue as necessary, which antibiotics should be started in this patient?
A. levofloxacin
B. vancomycin
C. doxycycline and ceftazidime
D. nafcillin and gentamicin
E. trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole(TMP-SMZ)
A 60-year-old morbidly obese man presents with complaints of fatigue, worsening exertional dyspnea, three-pillow orthopnea, lower extremity edema, and cough occasionally productive of frothy sputum. He has a long-standing history of type II diabetes and hypertension. On examination, you note the presence of bibasilar rales, an S3 gallop, jugular venous distention, and 2+ pitting edema in both legs up to the knees. There does not appear to be an arrhythmia present. Which of the following medications should be given initially?
A. metoprolol
B. diltiazem
C. furosemide
D. carvedilol
E. lisinopril
A19-year-old college student is found to have an elevated serum calcium on routine physical examination. She has a family history of hypercalcemia that has not resulted in any known symptoms. Further workup reveals a slightly elevated serum parathyroid hormone with depressed levels of serum phosphate. A 24hour urine calcium excretion is obtained and is low. Which of the following is the correct diagnosis?
A. familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH)
B. primary hyperparathyroidism
C. secondary hyperparathyroidism
D. tertiary hyperparathyroidism
E. metastatic bone cancer
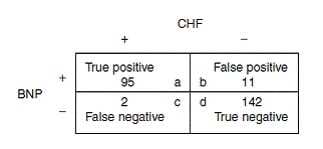
You are evaluating a journal article describing a test for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF). In the study described, 250 consecutive patients were given the test. Of the 250 subjects, 106 tested positive for CHF and 144 tested negative. All 250 subjects were then evaluated by expert cardiologists who were blinded to the results of the experimental test. These cardiologists determined that of the 106 persons who tested positive, 95 actually had CHF. Further, the cardiologists found that of the 144 who tested negative, 2 truly had CHF. What is the negative predictive value (NPV) of this test for the diagnosis of CHF?
A. 99%
B. 93%
C. 90%
D. 85%
E. 77%
The most likely cause of the pathologic findings in the spleen shown in Figure below is which of the following?
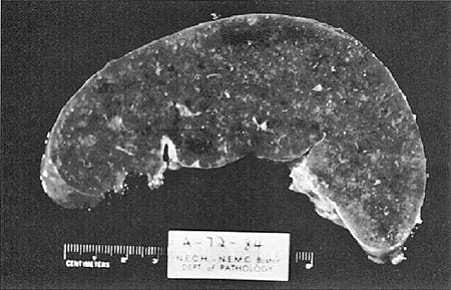
A. amyloidosis
B. metastatic carcinoma
C. septic infarct
D. Hodgkin disease
E. traumatic rupture
A 72-year-old male presented with nonspecific symptoms of easy fatigability, weight loss, and anorexia. On physical examination, generalized lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly were present. On the peripheral blood, he was found to have a marked lymphocytosis and in the serum, a small monoclonal spike was present. What would be the most likely histology seen in a lymph node biopsy?
A. reactive germinal centers
B. diffuse effacement of the normal architecture by a small lymphocytic population
C. diffuse architecture effacement with large cells with prominent nucleoli
D. a pleomorphic background composed of eosinophils, plasma cells, and small lymphocytes
E. a total replacement of the node by plasma cells
A 72-year-old male presented with nonspecific symptoms of easy fatigability, weight loss, and anorexia. On physical examination, generalized lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly were present. On the peripheral blood, he was found to have a marked lymphocytosis and in the serum, a small monoclonal spike was present. This disease is most prevalent in which age group?
A. teenagers
B. 2030 age group
C. 3040 age group
D. over 50 years
E. it may appear at any age
A 6-month-old male infant presents to your clinic because the mother is concerned that he is not eating well and he has been constipated. The mother tells you that her prenatal course and delivery were uneventful. On physical examination, the infant has a puffy face, large tongue, and persistent nasal drainage The above condition can be caused by a deficiency of which of the following?
A. iron
B. vitamin C
C. vitamin D
D. iodine
E. cortisol
A 67-year-old female was admitted to the hospital because of chronic fatigue and low back pain. An x-ray of the vertebral column showed diffuse osteoporosis and compression fractures of L1 and L2 vertebral bodies. The complete blood count (CBC) was within normal limits. The peripheral blood smear showed rouleaux formation. The immunoelectrophoresis showed a monoclonal spike of more than 3 g. A bone marrow biopsy was performed and showed an increase of more than 20% in plasma cells see Figure below
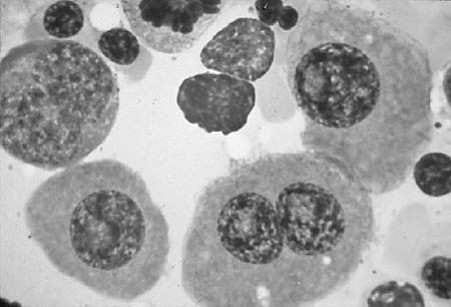
Radiographs of the bone and skeletal system in multiple myeloma will more characteristically show which of the following?
A. fractures
B. osteoblastic lesions
C. destructive bone lesions throughout the skeletal system
D. the skeletal system will remain intact
E. changes that resemble Paget disease