USMLE-STEP-1 Online Practice Questions and Answers
A newborn infant suffers from cyanotic heart disease caused by transposition of the great arteries (TGA). In this situation, the aorta arises from which of the following structures?
A. ductus arteriosus
B. left atrium
C. left ventricle
D. right atrium
E. right ventricle
The chief or peptic (zymogenic) cells of the gastric glands secrete pepsinogen. The latter is converted to pepsin, a 35-kilodalton (kDa) proteolytic enzyme, when the pH in the stomach falls below 5.0. In Following figure, which of the following arrows point to the location of chief or peptic (zymogenic) cells?
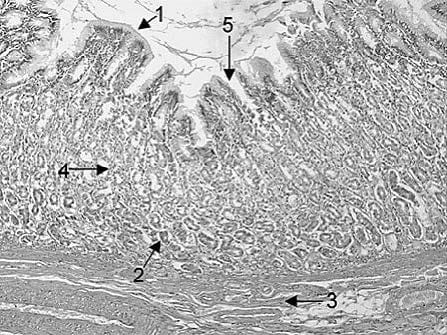
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
With increasing age, it is quite common for adults to have very low sensitivity for highpitch sounds. Which of the following physiologic responses occur as the pitch of a sound is increased at constant sound pressure?
A. a greater number of hair cells become activated
B. the amplitude of maximal basilar membrane displacement increases
C. the frequency of action potentials in auditory nerve fibers increases
D. the location of maximal basilar membrane displacement moves toward the cochlear base
E. units in the auditory nerve become responsive to a wider range of sound frequencies
Multiple sclerosis is a relatively common nervous system demyelinating disease. It is autoimmune and restricted to the central nervous system. Nerve conduction velocity is depressed in almost all affected individuals. Manipulations which prolong action potential duration seem to mitigate symptoms, possibly by facilitating conduction through sections of membrane which are no longer myelinated. Application of which type of drug might be expected to prolong action potential duration and thus be a potential therapeutic tool?
A. activates potassium channels
B. blocks L-type calcium channels
C. blocks potassium channels
D. blocks sodium channels
E. increases sodium channel inactivation
Below figure shows a quantitative precipitin curve of an antigen-antibody reaction, where the amount of antibody is kept constant throughout. According to the figure, which of the following statements is correct?
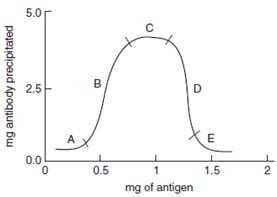
A. point A shows antigen excess
B. point B shows that there is no antibody formation
C. point C indicates that there is little, if any, free antigen and antibody in the reaction tube
D. point D represents the area of antigen destruction
E. point E indicates antibody excess
A 75-year-old lady is slowly developing a chronic suppurative cervicofacial lesion, thought to be actinomycosis. Which of the following is most likely to promote the progress of this infection?
A. high levels of oxygen in tissues
B. presence of a foreign body at the site of infection
C. production of exotoxin by A. israelii
D. production of leukocidin by A. israelii
E. production of pili by A. israelii
A 3-year-old child with a history of recurrent staphylococcal infections arrives at the emergency department at the local hospital. His neutrophils show normal chemotaxis, degranulation, and phagocytosis. However, intracellular killing of staphylococci by the neutrophils is severely impaired. Myeloperoxidase activity of his neutrophils is normal. The child has no history of streptococcal infection. Which of the following is the most likely disease affecting this patient? Which of the following explains the reason why the child described in question 530 has no history of streptococcal infection?
A. he has been administered antistreptolysin O
B. he has been immunized with CRP
C. he has been injected with pooled human gamma globulin
D. phagocytosis plays a minor role in the killing of streptococci
E. streptococci are catalase negative
A 57-year-old man seeks medical attention for the recent appearance of numerous, large, fluid-filled, cutaneous blisters. These involve the face, scalp, neck, and axillae. Manual pressure to the skin results in epidermal separation. These changes are most likely the result of which of the following?
A. autoimmune disorder
B. bacterial infection
C. dietary deficiency
D. exposure to a chemical toxin
E. local ischemia
Figure shows plasma concentrations of drug W in a patient following intravenous (IV) injection of a single dose of 10 mg of the drug, an agent eliminated from the body by renal excretion. At hour 12, the patient is treated with sodium bicarbonate (arrow).
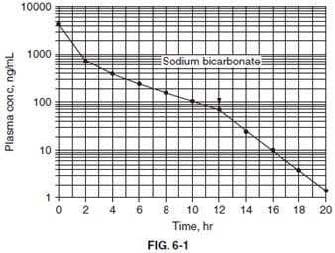
Use the data before hour 12 to calculate the half-life ( ) for drug W.

A. 0.5 hour
B. 1 hour
C. 3 hours
D. 7 hours
E. 10 hours
A patient has begun exhibiting signs of paranoia and psychosis within the past week. In considering the diagnosis of schizophrenia, which of the following is a crucial piece of information?
A. The patient does not smoke.
B. The patient has a history of similar psychotic episodes in the past.
C. The patient has a history of substance abuse.
D. The patient is a toxicologist.
E. The patient is single.