NSE5_FMG-5.4 Online Practice Questions and Answers
View the following exhibit:

Which one of the following statements is true regarding the object named ALL?
A. FortiManager updated the object ALL using FortiManager's value in its database.
B. FortiManager updated the object ALL using FortiGate's value in its database.
C. FortiManager created the object ALL as a unique entity in its database, which can be only used by this managed FortiGate.
D. FortiManager installed the object ALL with the updated value.
View the following exhibit:
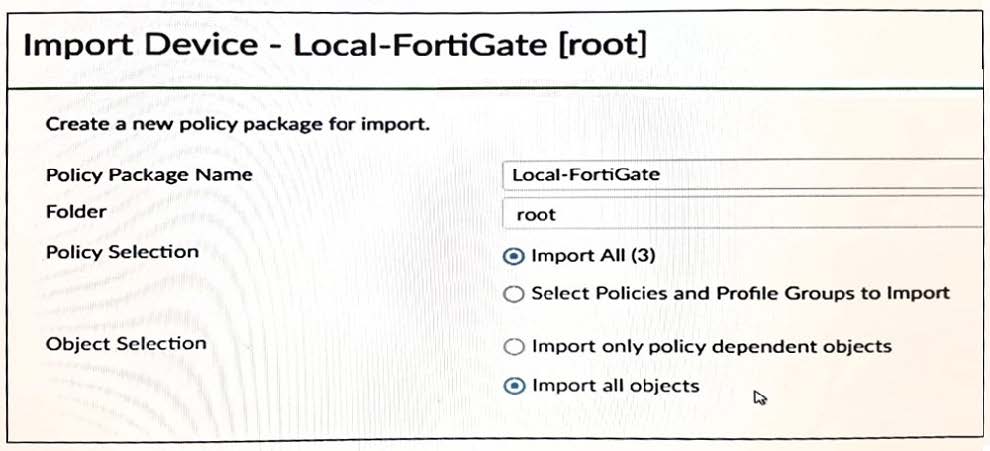
An administrator is importing a new device to FortiManager and has selected the shown options.
What will happen if the administrator makes the changes and installs the modified policy package on this managed FortiGate?
A. The unused objects that are not tied to the firewall policies will be installed on FortiGate.
B. The unused objects that are not tied to the firewall policies will remain as read-only locally on FortiGate.
C. The unused objects that are not tied to the firewall policies in policy package will be deleted from the FortiManager database.
D. The unused objects that are not tied to the firewall policies locally on FortiGate will be deleted.
Which of the following conditions trigger FortiManager to create a new revision history? (Choose two.)
A. When FortiManager installs device-level changes to a managed device.
B. When configuration revision is reverted to previous revision in the revision history.
C. When changes to device-level database is made on FortiManager.
D. When FortiManager is auto-updated with configuration changes made directly on a managed device.
Which of the following statements are true regarding an FGFM keepalive message? (Choose two.)
A. It includes the configuration checksum of FortiGate.
B. The keepalive interval for keepalive messages is configured on FortiGate.
C. It is sent only by FortiGate.
D. It is used between FortiManager HA cluster members to make sure cluster members are in sync.
As a result of enabling FortiAnalyzer features on FortiManager, which one of the following statements is true?
A. FortiManager can be used only as a logging device.
B. FortiManager will enable ADOMs automatically to collect logs from non-FortiGate devices.
C. FortiManager will send the logging configuration to the managed devices so the managed devices will start sending logs to FortiManager.
D. FortiManager will reboot.
Which of the following statements are true regarding ADOM revisions? (Choose two.)
A. ADOM revisions can save the current state of all policy packages and objects for an ADOM.
B. ADOM revisions can significantly increase the size of the configuration backups.
C. ADOM revisions can create System Checkpoints for the FortiManager configuration.
D. ADOM revisions can save the current state of the whole ADOM.
What configuration setting for FortiGate is part of a device-level database on FortiManager?
A. Routing
B. Security profiles
C. VIP and IP Pools
D. Firewall policies
In addition to the default ADOMs, an administrator has created a new ADOM named Training for FortiGate devices. The administrator sent a device registration request to FortiManager from a remote FortiGate. Which one of the following statements is true?
A. The FortiGate will be automatically added to the Training ADOM.
B. By default, the unregistered FortiGate will appear in the root ADOM.
C. The FortiManager administrator must add the unregistered device manually to the Training ADOM using the Add Device wizard.
D. The FortiGate will be added automatically to the default ADOM named FortiGate.
An administrator's PC crashed before the administrator could submit a workflow session for approval. After the PC restarted, the administrator noticed that the ADOM was locked from the session before the crash. How can the administrator unlock the ADOM?
A. The administrator must log in as Super_User in order to unlock the ADOM.
B. The administrator must restore the configuration from a previous backup.
C. Delete the previous admin session manually through the FortiManager's GUI or CLI.
D. The administrator must log in using the same administrator account to unlock the ADOM
An administrator has enabled Service Access on FortiManager. What is the purpose of Service Access on the FortiManager interface?
A. Allows FortiManager to run real-time debugs on the managed devices.
B. Allows FortiManager to respond to requests for FortiGuard services from FortiGate devices.
C. Allows FortiManager to automatically configure a default route.
D. Allows FortiManager to download IPS packages.