HPE6-A49 Online Practice Questions and Answers
What is one customer requirement that can drive the need for a relatively dense AP deployment, in which the coverage areas of at least three AP radios overlap?
A. support for beacon management
B. AP operation as hybrid AMs for IDS/WIPS
C. the deployment of dual 5GHz radio APs
D. location tracking of wireless IoT devices
A customer has Aruba network infrastructure devices that could be managed by either Aruba Central or
Aruba AirWave.
Which customer characteristic should point the architect toward an AirWave recommendation as opposed
to a Central recommendation?
A. desire to lease managed services on an ongoing basis
B. small IT staff and preference for cloud solutions
C. policies that network management occurs on premises
D. need to support Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
Refer to the exhibit.
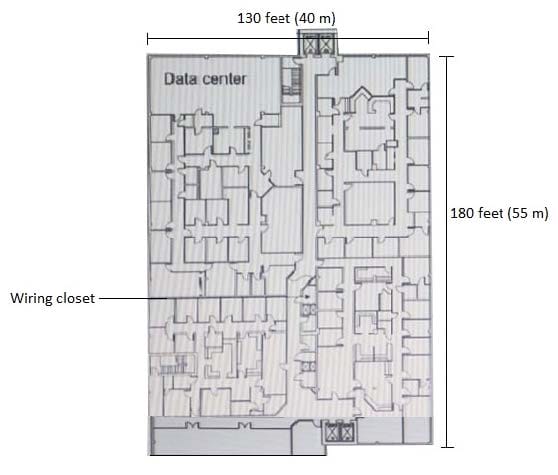
The customer requires a solution for the writing closet shown in the exhibit. The closet serves the entire floor, which is wired for CAT5e cable. The closet has four CAT5e cables to the data center 110 feet (34 m) away. The switch or switches in this closet will need to support 100 wired endpoints and 16 AP-345s. The switch or switches must connect to the network core, Aruba 5406R switches, in the data center on uplinks that provide at least 20 Gbps bandwidth total.
What is one benefit of an Aruba solution for meeting these requirements?
A. AOS-Switches can meet the uplink bandwidth needs with an extensive array of choices for transceivers.
B. Aruba PoE+ ports can provide more than 30W of power even to APs at the fat end of the floor.
C. Aruba Smart Rate ports enable switches to achieve the required uplink speeds without expensive re-cabling.
D. Aruba conditioning mode cables enable 10GbE SFP+ of 40GbE QSFP+ connections on copper cabling.
Refer to the exhibit.
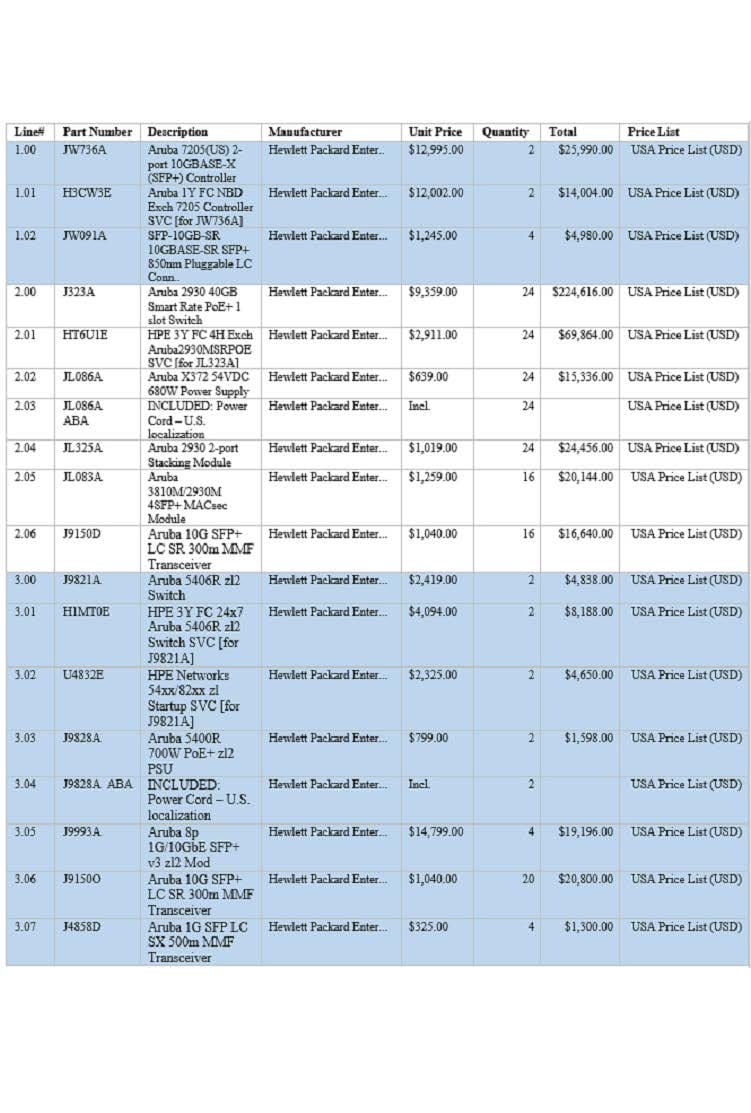
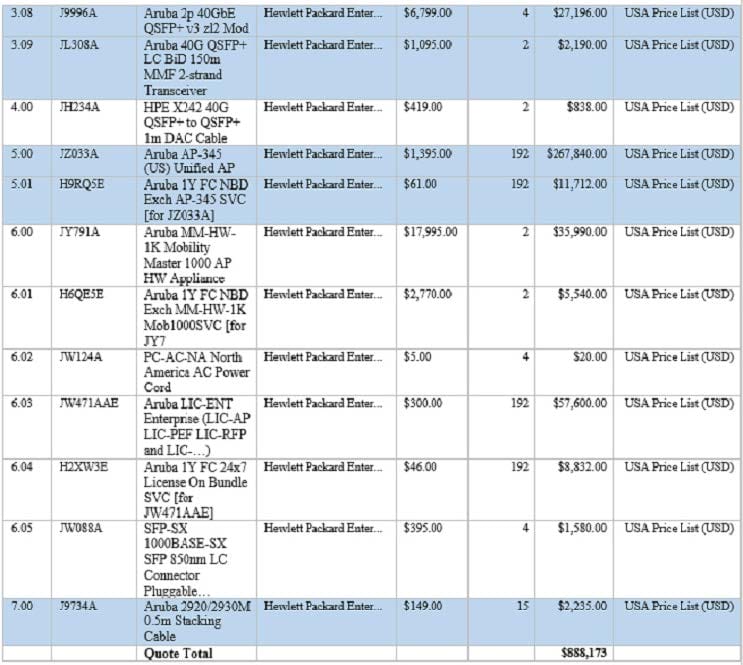
The network architect has created the BOM shown in the exhibit for a complete new wired and wireless solution for a customer. This solution will support 6000 wireless clients and 900 wired clients. The customer wants to discover and manage every component of the network in AirWave, including MMs, MCs, APs, and switches.
How many AirWave licenses does the architect need to add?
A. 30
B. 222
C. 6930
D. 7122
Refer to the exhibit.
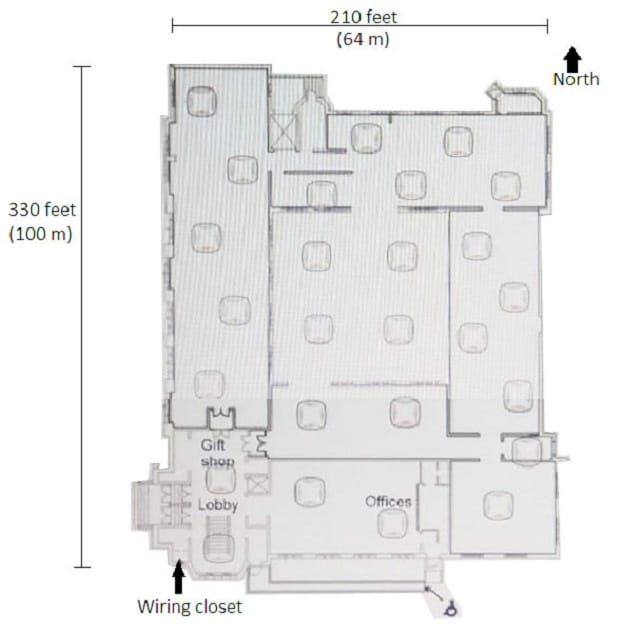
A museum wants to add full 802.11ac wireless coverage across the building, which is about 210 feet (64 m) by 330 feet (100m). The museum has 15-foot (4,6 m) ceilings and stone interior walls. The network needs to support up to 600 wireless guest devices. The exhibit also shows a preliminary plan for AP locations. The museum has eight Ethernet drops in the lobby and gift shop, but has otherwise not been wired.
What is one recommendation that the architect should make to ensure a successful deployment?
A. use of directional antennas to avoid lost signal
B. addition of a writing closet closer to the north side
C. use of at least CAT5 cable to connect to the APs
D. addition of about 10 APs to achieve adequate density
A university has a dormitory with several floors. Currently APs are deployed in the hallways about every 50
feet (15m). The university has several issues with the existing network:
Students complain that the network is very slow, and the wireless signal is poor.
Students want to connect some equipment such as gaming consoles and IP TVs on Ethernet, but the dorm
rooms just have one Ethernet port.
How does the deployment of AP303Hs resolve the customer issues?
A. They are specialized to provide wireless coverage for single-room deployment and also provide wired ports for clients.
B. They are specialized for wireless meshing, which conserves Ethernet ports, and for high-speed wireless services.
C. They have high-gain antennas designed for older buildings and support Smart Rate for high bandwidth on one port.
D. They have directional antennas that will improve the wireless signal and require just one Ethernet port.
A network architect plans to propose a virtual Mobility Master (VMM) for a new solution. The solution will support up to 4,800 wireless client devices and include: two Virtual Mobility Controllers (VMCs) in a cluster 180 APs
Which licenses should the architect propose?
A. 1 MM-VA-500; 2 MC-VA-250; 540 Enterprise licenses
B. 1 MM-VA-500; 1 MC-VA-250; 180 Enterprise licenses
C. 1 MM-VA-1K; 2 MC-VA-250; one Enterprise license
D. 1 MM-VA-1K; 1 MC-VA-250; 180 Enterprise licenses
A customer has an existing Aruba wireless solution to provide wireless access for employees. The solution includes APs, mobility controllers (MCs) at the network core, and a Mobility Master (MM). A customer would like to set up a separately managed guest network and have the traffic go directly to the DMZ.
What should the architect suggest as the simplest solution that meets the requirements?
A. Add APs in a dedicated AP group to support only the guest network SSID.
B. Have a dedicated mobility controller in the DMZ managed by the same MM.
C. Double the number of APs and controllers
D. Use MultiZone, and put a mobility controller in the DMZ.
What is one requirement for ensuring that MCs can update their software without the need for a maintenance window?
A. MCs must be managed by an MM and connected to the same switch.
B. MCs must be in a cluster and connected in the same VLANs.
C. MCs must be directly connected on at least one port.
D. MCs must have AP licenses assigned to them in a dedicated local pool.
Refer to the exhibit.
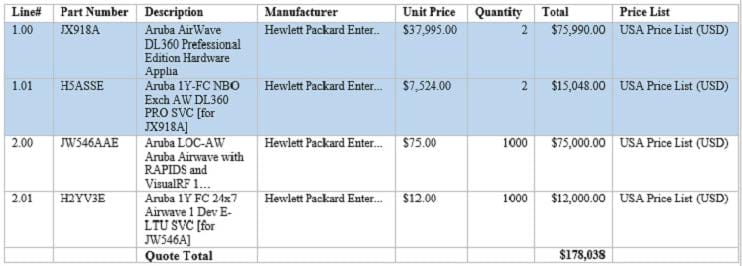
A customer needs an AirWave solution that can manage 1000 devices. The customer wants a hardware
solution and active/standby redundancy for the solution.
The exhibit shows the BOM that the architect has created.
Which corrections should the architect make?
A. Change the active appliance to an Enterprise appliance.
B. Add 1000 additional AirWave managed device licenses.
C. Change both of the appliances to Enterprise appliance.
D. Add a failover license for 1000 managed devices.