HPE6-A41 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Refer to the exhibit.
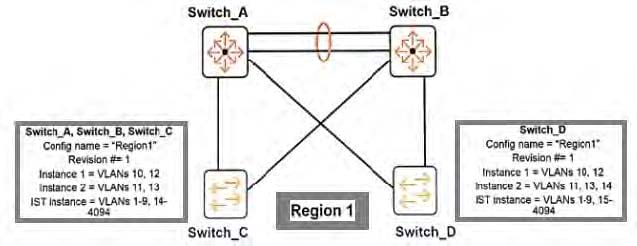
Originally, all four switches had the same region configuration. VLAN 14 was added to Switch_D and then mapped to instance 2.
How does this affect the MSTP topology?
A. Load sharing is lost, one of the uplinks is blocked for all traffic on Switch_C and Switch_D.
B. Load sharing is lost, one of the uplinks is blocked for all traffic on Switch_D
C. All connectivity is lost, both uplinks are blocked on Switch_D.
D. A Layer 2 loop exists and will cause sporadic connectivity issues.
Refer to the exhibit.
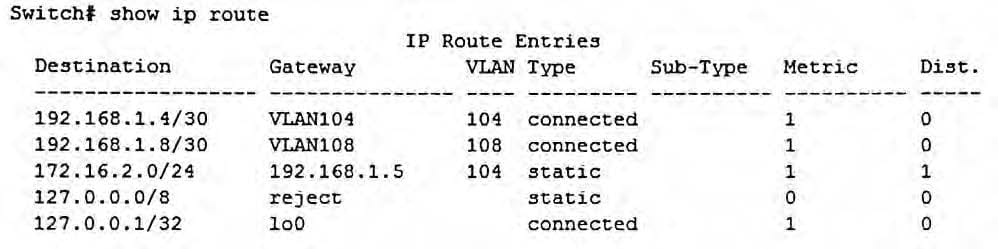
The network administrator enters this command:
Switch(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0/30 192.168.1.100 metric 1 distance 1
Why does this route fail to appear in the IP routing table?
A. Its prefix length is invalid.
B. Its next hop is unreachable.
C. Its administrative distance is the same as an existing static route.
D. Its metric is the same as an existing static route.
Refer to the exhibit. Exhibit 1.
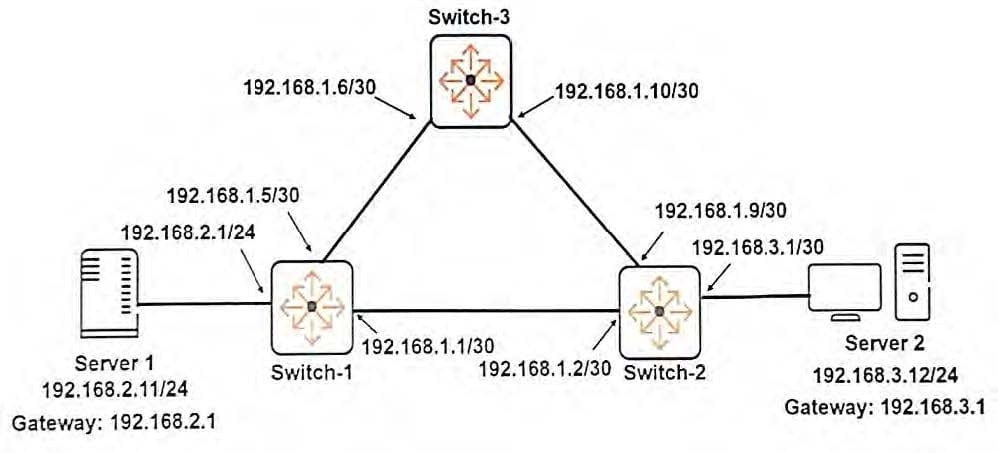
Exhibit 2.
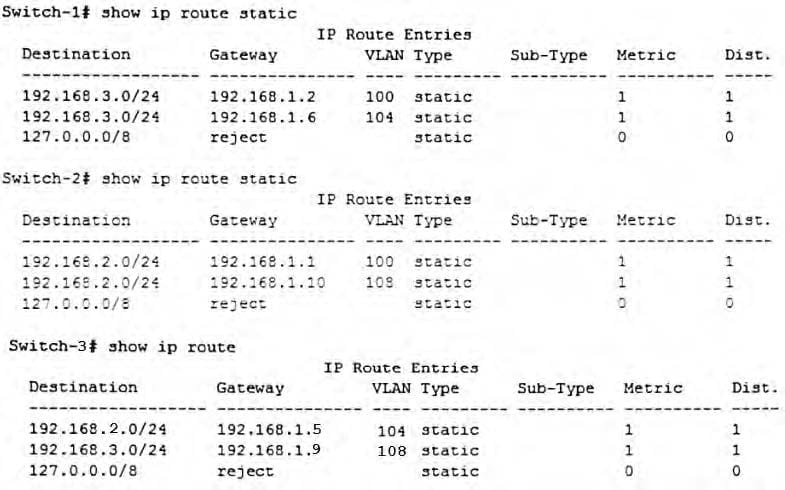
The routing configuration must support this behavior:
Server 1 and Server 2 communicate over Link 1 when Link 1 is up.
If Link 1 fails, Server 1 and Server 2 can continue to communicate over the path through Switch-3.
What must the network administrator change to meet these criteria?
A. On Switch 3, add a route to 192.168.2.0/24 through 192.168.1.9 and a route to 192.168.3.0/24 through
192.168.1.5.
B. On Switch-1, Switch-2, and Switch-3, change the next hop in each static route to specify an IP address that exists on that switch.
C. On Switch-1, raise the administrative distance for the second route to 192.168.3.0/24; on Switch-2, raise the administrative distance for the second route to 192.168.2.0/24
D. On Switch-1, add a route to 192.168.1.8/30 through 192.168.0.3; on Switch-2, add a route to 192.168.1.4/30 through 192.168.1.1; on Switch-3, add a route to 192.168.1.0/30 through 192.169.1.4.
E. On Switch-1, add a route to 192.168.1.8/30 through 192.168.1.2; on Switch-2, add a route to 192.168.1.4/30 through 192.168.1.1; on Switch-3, add a route to 192.168.1.0/30 through 192.168.1.4.
How does a switch treat a link aggregation?
A. The switch treats the link aggregation as one logical link for spanning tree, but it learns MAC addresses separately on each individual interface within the aggregation.
B. The switch treats the link aggregation as one logical link. It assigns one spanning tree port role to the link aggregation, and it learns MAC addresses on the aggregation.
C. The switch treats the link aggregation as one logical link for MAC learning, but it assigns an individual spanning tree port role to each interface within the aggregation.
D. The switch treats each interface within the interface as a separate entity for MAC address learning; it also assigns an individual spanning tree port role to each interface.
A network administrator just received two switches and wants to use the plug-and-play method to establish a Virtual Switching Framework (VSF) fabric with the fewest steps possible.
What must the administrator do to establish the fabric in this way?
A. Configure a VSF link on the commander, and enable VSF on the standby member.
B. Configure a VSF link on the commander, and enable VSF on the commander.
C. Enable VSF on both me commander and the standby member.
D. Configure a VSF link on both the commander and the standby member.
A network administrator discovers and then authorizes several ArubaOS switches in Aruba AirWave. Immediately after the administrator authorizes the switches, AirWave cannot communicate with the switches anymore.
What should the administrator do to restore communication?
A. Change the SNMP and Telnet/SSH credentials in the AirWave global communication settings to match those on the switches.
B. Change the management level for the switches to Monitoring and Firmware Updates Only.
C. Specify the SNMP and Telnet/SSH credentials on the switches to update the individual communication settings on the switches.
D. Change the management level for the switches to Manage Read/Write.
A manager password is configured on an ArubaOS switch. The network administrator wants to ensure managers only use SSH to connect to the ArubaOS switch for CLI access. Which step should the administrator complete to accomplish this?
A. Enter the command no telnet-server.
B. Enter the commend include-credentials.
C. Enter the command ip ssh.
D. Enter the command secure-vty.
A network administrator enters this command on an ArubaOS switch with IP routing enabled:

This is the only IP route to 0.0.0.0/0 on the switch.
What is the effect?
A. The switch uses this route to route all traffic from 10.1.1.1.
B. The switch uses this route for all traffic unless the traffic matches a route with a lower cost than 10.
C. The switch uses this route for all traffic unless the traffic matches a route with a lower administrative distance than 10.
D. The switch uses this route for all traffic that does not match a specific route in its routing table.
Which security options for a WLAN can authenticate either the computer or the user?
A. Open with MAC authentication
B. MAC authentication with WPA2 Enterprise (802.1X) fail-thru
C. Personal (preshared key) authentication with WEP
D. Personal (preshared key) authentication with WPA2
Which security option for a WLAN provides the best access control security?
A. MAC authentication with WPA-PSK
B. WPA2 Enterprise (802.1X)
C. WPA2 Personal (preshared key)
D. MAC authentication with WPA2 Enterprise (802.1X) fail-thru