FINANCIAL-ACCOUNTING-AND-REPORTING Online Practice Questions and Answers
Income tax-basis financial statements differ from those prepared under GAAP in that income tax-basis financial statements:
A. Do not include nontaxable revenues and nondeductible expenses in determining income.
B. Include detailed information about current and deferred income tax liabilities.
C. Contain no disclosures about capital and operating lease transactions.
D. Recognize certain revenues and expenses in different reporting periods.
At December 31, 1998, Off-Line Co. changed its method of accounting for demo costs from writing off the costs over two years to expensing the costs immediately. Off-Line made the change in recognition of an increasing number of demos placed with customers that did not result in sales. Off-Line had deferred demo costs of $500,000 at December 31, 1997, $300,000 of which were to be written off in 1998 and the remainder in 1999. Off-Line's income tax rate is 30%. In its 1998 financial statements, what amount should Off-Line report as cumulative effect of change in accounting principle?
A. $0
B. $200,000
C. $350,000
D. $500,000
How should the effect of a change in accounting principle that is inseparable from the effect of a change in accounting estimate be reported?
A. As a component of income from continuing operations.
B. By restating the financial statements of all prior periods presented.
C. As a correction of an error.
D. By footnote disclosure only.
Which of the following should be disclosed in a summary of significant accounting policies?
A. Basis of profit recognition on long-term construction contracts.
B. Future minimum lease payments in the aggregate and for each of the five succeeding fiscal years.
C. Depreciation expense.
D. Composition of sales by segment.
There are multiple active markets for a financial asset with different observable market prices: There is no principal market for the financial asset. What is the fair value of the asset?
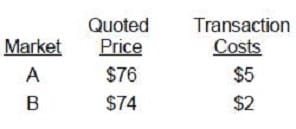
A. $71
B. $72
C. $74
D. $76
Goddard has used the FIFO method of inventory valuation since it began operations in 1987. Goddard decided to change to the weighted-average method for determining inventory costs at the beginning of 1990. The following schedule shows year-end inventory balances under the FIFO and weighted-average methods:
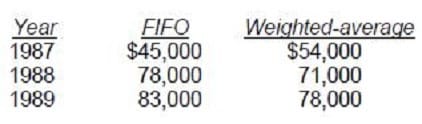
What amount, before income taxes, should be reported in the 1990 retained earnings statement as the
cumulative effect of the change in accounting principle?
A. $5,000 decrease.
B. $3,000 decrease.
C. $2,000 increase.
D. $0.
While preparing its 1991 financial statements, Dek Corp. discovered computational errors in its 1990 and 1989 depreciation expense. These errors resulted in overstatement of each year's income by $25,000, net of income taxes. The following amounts were reported in the previously issued financial statements: Dek's 1991 net income is correctly reported at $180,000. Which of the following amounts should be reported as prior period adjustments and net income in Dek's 1991 and 1990 comparative financial statements?


A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Tack, Inc. reported a retained earnings balance of $150,000 at December 31,1990. In June 1991, Tack discovered that merchandise costing $40,000 had not been included in inventory in its 1990 financial statements. Tack has a 30% tax rate. What amount should Tack report as adjusted beginning retained earnings in its statement of retained earnings at December 31, 1991?
A. $190,000
B. $178,000
C. $150,000
D. $122,000
On June 30, 1991, Mill Corp. incurred a $100,000 net loss from disposal of a component of a business. Also, on June 30, 1991, Mill paid $40,000 for property taxes assessed for the calendar year 1991. What amount of the foregoing items should be included in the determination of Mill's net income or loss for the six-month interim period ended June 30, 1991?
A. $140,000
B. $120,000
C. $90,000
D. $70,000
On January 2, 1993, Quo, Inc. hired Reed to be its controller. During the year, Reed, working closely with
Quo's president and outside accountants, made changes in accounting policies, corrected several errors
dating from 1992 and before, and instituted new accounting policies.
Quo's 1993 financial statements will be presented in comparative form with its 1992 financial statements.
This question represents one of Quo's transactions. List B represents the general accounting treatment
required for these transactions. These treatments are:
•
Cumulative effect approach - Include the cumulative effect of the adjustment resulting from the accounting change or error correction in the 1993 financial statements, and do not restate the 1992 financial statements.
•
Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach - Restate the 1992 financial statements and adjust 1992 beginning retained earnings if the error or change affects a period prior to 1992.
•
Prospective approach - Report 1993 and future financial statements on the new basis but do not restate 1992 financial statements.
Item to Be Answered During 1993, Quo determined that an insurance premium paid and entirely expensed in 1992 was for the period January 1, 1992, through January 1, 1994.
List B (Select one)
A. Cumulative effect approach.
B. Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach.
C. Prospective approach.


