CTAL-TM_SYLL2012 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Consider an information system of a Pay-Tv company based on a SOA architecture. The integrated system currently consists of three core systems:
-
a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system
-
a BRM (Billing and Revenue Management) system
-
a CAS (Conditional Access System) system all of them communicating with SOA Middleware.
You have been asked to manage the testing activities for the integration of two additional off-the- shelf systems from two different vendors: a SMS (Short Message Service) server and an IVR (Interactive Voice Response) system.
Assume that there is a high likelihood that the two off-the-shelf systems will be low-quality and that you have a clear proof that the testing performed by the two vendors on their systems has been unsystematic and unprofessional. This
obviously leads to higher quality risk for the overall integrated system.
You are the Test Manager of this project. Your main goal is to plan for testing activities to mitigate this risk.
Which of the following answers best describes the test activities (assuming it is possible to perform all of them) you should plan for?
A. You should plan for an informal and minimal acceptance test of the two off-the-shelf systems and then a single end-to-end test of the overall integrated system
B. You should directly plan for a single end-to-end test focused on end-to-end tests of the overall integrated system without an acceptance test of the two off-the-shelf systems
C. You should plan for two levels: a system integration test and an end-to-end test of the overall integrated system
D. You should plan for adequate re-testing of both the systems followed by a system integration test and an end-to-end test of the overall integrated system
Assume you are currently working on a project developing a system where functional requirements are very well specified. Unfortunately non-functional requirements do almost not exist.
You are the Test Manager. You have to choose a technique for test selection that allows testing of non-functional characteristics, especially reliability.
Which of the following techniques for test selection do you expect being most useful in this scenario?
A. A model-based technique based on the creation of operational profiles
B. Ambiguity reviews
C. Test condition analysis
D. Cause-effect graphing
In the test strategy document your organization declares:
-
To adopt a V-model development lifecycle, with three formal levels of testinG. unit, integration and system testing
-
To use a blended risk-based and regression-averse testing strategy for each level of testing
The following is an excerpt of the "approach" section for the system test plan document of a new project:
"Testing will only use manual tests. Due to the short period of time for test execution, the following activities will be performed in parallel with test execution: Test planning, test analysis and test design.
Basic metrics will be taken for test effort (i.e. person-hours), test cases executed (passed/failed), and incidents (no more metrics, such as code coverage, will be collected)."
In the system test plan, no deviations from the test strategy are described.
Based only on the given information, which of the following statements is true?
A.
The approach described in the system test plan document is consistent with the test strategy
B.
The approach described in the system test plan document is consistent with the risk-based testing strategy, but it is inconsistent with the regression testing strategy
C.
The approach described in the system test plan document is consistent with the regression testing strategy, but it is inconsistent with the risk-based testing strategy
D.
The approach described the system test plan document is inconsistent with both the risk-based and regression testing strategies
Which of the following answers describes a factor that may reduce the effort spent when using distributed test teams without negatively affecting system quality?
A. Difficulties in communication between the distributed test teams due to time zone differences
B. With several distributed test teams, every team assumes that some test conditions are covered by other teams but actually no one covers them
C. With several distributed test teams, two or more teams assume some test conditions are covered by their team and their team alone. But all of the teams actually cover them
D. With several distributed test teams, all of the distributed test teams use a single unified test dashboard
You are the Test Manager of a project that adopts a V-model with four formal levels of testinG.
unit, integration, system and acceptance testing.
On this project reviews have been conducted for each development phase prior to testing, which is to say that reviews of requirements, functional specification, high-level design, low-level design and code have been performed prior to
testing.
Assume that no requirements defects have been reported after the release of the product.
Which TWO of the following metrics do you need in order to evaluate the requirements reviews in terms of phase containment effectiveness?
A. Number of defects found during the requirements review
B. Total number of defects attributable to requirements found during unit, integration, system and acceptance testing
C. Total number of defects found during functional specification review, high-level design review, low-level design review, code review, unit testing, integration testing, system testing and acceptance testing
D. Time to conduct the requirements review
E. Total number of defects attributable to requirements, found during functional specification review, high-level design review, low-level design review, code review, unit testing, integration testing, system testing and acceptance testing
Consider the following statements describing the importance of improving the test process:
I. Test process improvement is important because being focused only on the test process it can provide recommendations to improve the test process itself, but it can't indicate or suggest improvement to areas of the development process
II. Test process improvement is important because it is much more effective than software process improvement to improve the quality of a software system
III. Test process improvement is important because several process improvement models (STEP, TPI Next, TMMi) have been developed over the years
IV.
Test process improvement is important because every organization, regardless of the context, should always achieve the maximum level of maturity of testing described in the test improvement models such as TMMi Which of the following answers is correct?
A.
I. and IV. are true; II. and III. are false
B.
I., II., III. and IV are false
C.
I., II. and III are true; IV. is false
D.
I., II. and III. are false; IV. is true
After the presentation, you are asked to explain the chart. Assume you have applied a full risk-based testing strategy.
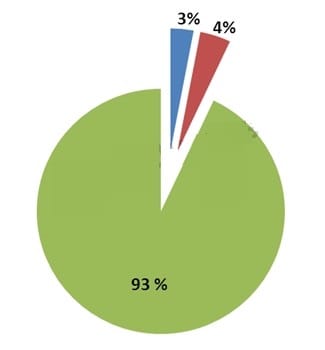
Which of the following answers would you expect to best describe the pie chart?
A. All the risk items have been covered with tests. No more risk items remain to test
B. According to the full risk-based testing strategy applied, it is very likely that the highest-risk items, tests and bugs remain in the blue and red areas. Therefore, it is very risky to release the application
C. Only the lowest-risk items, tests and bugs should remain in the blue and red areas. Therefore the application can be released at any time subject to management of the items identified in those areas
D. 97 percent of the risk items has been tested. No open bugs or test failures remain. Only 3 percent of risk items remains to be covered by the remaining test
In your organization the following tools of the same vendor are currently in usE. a requirements management tool, a test management tool and a bug tracking tool.
You are the Test Manager.
You are currently evaluating a test automation tool of the same vendor (to complete the vendor's tool suite) against an interesting open-source test automation tool under the GNU GPL (General Public License).
There are no initial costs associated to that open-source tool.
Which of the following statements associated to the selection of the open-source tool is correct in this scenario?
A. The open-source tool can be modified but only if the community of developers of that tool gives you the formal permission to modify it
B. There are no initial costs for the open-source tool but you should carefully consider the costs associated to the integration with the existing tools and also evaluate the recurring costs
C. There are no initial costs for the open-source tool because open-source tools are usually low- quality, while vendor tools have always a better quality than the corresponding open-source tools
D. The open-source tool can be modified but it can't be distributed further in any way
Which of the following would you expect to be most likely an example of a motivating factor for testers?
A. The resources allocated for the testing activities are not sufficient and don't allow the testers to contribute to the quality of the product
B. The testers contribution to the quality of the software products developed from an organization is recognized with increased responsibilities
C. The same regressions tests are executed manually by the same testers, for every product release, without any progression in content
D. The testers are asked to perform, in parallel with their testing tasks, other tasks unrelated to their testing responsibilities
Which of the following would you expect to be most likely an example of a demotivating factor for testers?
A. The management asks the testers to be kept informed about the intensity, quality and results of testing
B. The testers' recommendations to improve the system or its testability are adopted by the development team
C. The same regressions tests are manually executed by the same testers, for every product release, without regression test tools
D. The testers are assessed on whether and how often they detect important and critical failures
E. Test quality is measured by counting the number of customer/user reported problems.