ACLS Online Practice Questions and Answers
T/F: Infectious complications of intravenous cannulas should be prevented by using systemic antibiotics.
A. True
B. False
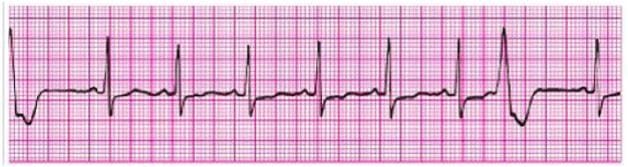
A patient in the ED develops recurrent chest discomfort (8/10) suspicious for ischemia. His monitored rhythm becomes irregular as seen above. Oxygen is being administered by nasal cannula at 4 L/min and an intravenous line is patent. Blood pressure is 160/96 mmHg. There are no allergies or contraindications to any medication. You would first order
A. Lidocaine 1 mg/kg IV and infusion 2 mg/min
B. Morphine sulfate 2 to 4 mg IV
C. Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg SL
D. Amiodarone 150 mg IV
E. Intravenous nitroglycerin initiated at 10 ug/min and titrated
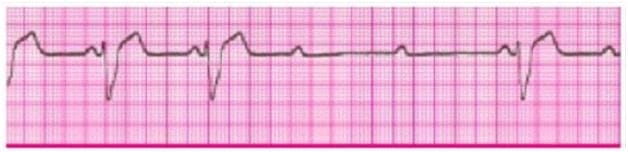
You are monitoring this patient after successful resuscitation. You note the above rhythm on the cardiac monitor and document a rhythm strip for the patient's chart. She has no complaints and blood pressure if 110/70 mmHg.
Now you would:
A. Give Atropine 1 mg IV
B. Give Atropine 0.5 mg IV
C. Administer sedation and begin immediate transcutaneous pacing at 80 per minute
D. Start dopamine 2 to 10 ug/kg per minute and titrate heart rate
E. Prepare for transcutaneous pacing (place pacing pads, do not pace)
Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the administration of vasopressin during cardiac arrest?
A. Vasopressin can be administered twice during cardiac arrest
B. Vasopressin is indicated for VF and pulseless VT prior to the delivery of the first shock
C. The correct dose of Vasopressin is 40 U administered IV or IO
D. Vasopressin is recommended instead of epinephrine for the treatment of asystole
T/F: An automated defibrillator can accurately diagnose ventricular fibrillation during chest compressions.
A. True
B. False
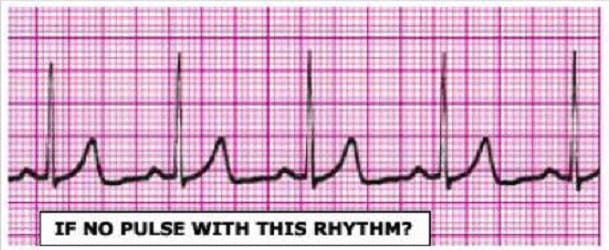
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
SIMULATION
Describe the use of a curved versus straight laryngoscope blade.
A. The curved blade is designed to fit into the vallecula, whereas the straight blade is used to lift the epiglottis.
FILL BLANK
What is the effect of a dopamine infusion at greater than 5 mcg/kg/min?
A. Peripheral artery vasoconstriction.
SIMULATION
How does the trachea in an adult and child differ?
A. Infants and children have narrower tracheas that are obstructed more easily by swelling, and the trachea is also softer and more flexible. The cricoid cartilage is less developed and less rigid, and is the narrowest portion of the child's airway.
FILL BLANK
If while ventilating a patient the chest does not rise and fall, what should you do after repositioning fingers and mask?
A. Check for obstruction