4A0-M10 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements about QoS profiles used in 5G is FALSE?
A. SMF derives the QoS profile of a QoS Flow from a PCC rule and sends it to NG-RAN.
B. NG-RAN uses the QoS profiles to create mapping between QoS Flow IDs and data radio bearers.
C. NG-RAN sends the QoS profiles and corresponding QoS Flow IDs to the UE.
D. Each QoS profile includes a 5G QoS Identifier (5QI) and an Allocation and Retention Priority (ARP).
Which of the following statements about network slice selection assistance information (NSSAI) is FALSE?
A. Allowed NSSAI is a set of slices provided to UE by AMF during UE registration procedure.
B. Requested NSSAI is a set of slices provided by UE to the network and contains values from serving PLMN.
C. Subscribed NSSAI is a set of slices specified in the UE subscription data and contains only home PLMN values.
D. Configured NSSAI is a set of slices configured on the AMF and contains slices supported per tracking area.
Which of the following best describes a UE route selection policy (URSP)?
A. A URSP is a policy pre-configured in the UE. The UE uses this policy to select a non-3GPP access network and an N3IWF to use in the PLMN.
B. A URSP is a policy provisioned to AMF by PCF. The AMF uses this policy to select an SMF that can serve a given PDU session for the UE.
C. A URSP is a policy that can be pre-configured in the UE or provisioned to the UE by PCF. The UE uses this policy to determine how to handle a given application.
D. A URSP is a policy pre-configured on the SMF. The SMF uses this policy to select a UPF that can serve a given PDU session for the UE.
A UE triggers an initial registration procedure to use services offered by a 5G network. Which of the following actions is NOT performed as a result of this procedure?
A. AMF interacts with AUSF to authenticate the UE.
B. AMF interacts with PCF to create an AM (access and mobility) policy association.
C. AMF retrieves the UE AM (access and mobility) and SM (session management) data from UDM.
D. AMF allocates a 5G-GUTI and includes it in the Registration Accept message sent to UE.
A connected UE moves from 5GS to EPS using the inter-system handover procedure with N26 interface. Which of the following actions is NOT performed?
A. Source gNB sends an NGAP Handover Required message to source AMF with handover type set to “NRtoLTE”.
B. Source AMF obtains session management contexts stored in UDM+HSS for each PDU session that supports interworking.
C. Source AMF sends a Forward Relocation Request message to the target MME and provides session management contexts.
D. Indirect downlink data forwarding paths are established from source gNB to target eNodeB.
An AMF needs to know when an SMF deregisters with the NRF. Which of the following NRF APIs should the AMF use?
A. Nnrf_NFManagement_NFUpdate Request
B. Nnrf_NFDiscovery_NFDiscover Request
C. Nnrf_NFManagement_NFStatusSubscribe Request
D. Nnrf_NFManagement_NFDeregister Request
The exhibit below displays a packet capture of the PFCP Session Modification Request message sent during a PDU Session Establishments procedure. What do the highlighted TEID and IP Address refer to?
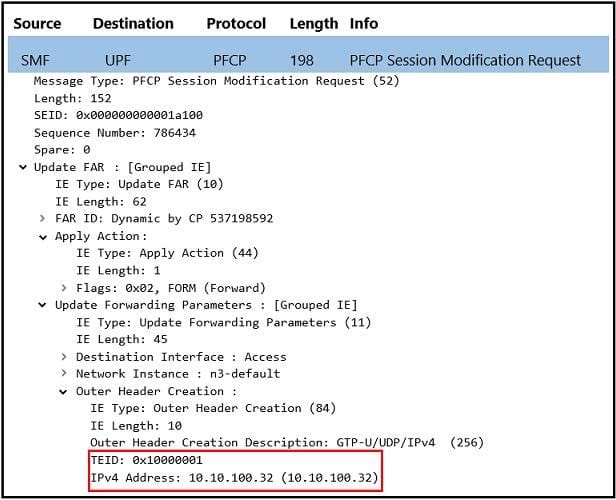
A. The N3 TEID allocated by gNB and the gNB IP address.
B. The N3 TEID allocated by UPF and the UPF IP address.
C. The N3 TEID allocated by SMF and the SMF IP address.
D. The N3 TEID allocated by SMF and the UPF IP address.
When an idle UE moves from EPS to 5GS, which procedure is performed?
A. Registration
B. Tracking Area Update
C. Initial Attach
D. Service Request
Which of the following statements about 5GS PDU sessions is FALSE?
A. A PDU session allows for the exchange of PDUs between UE and a data network.
B. A PDU session contains one single dedicated radio bearer and one or more N3 GTP-U tunnels.
C. A PDU session has one default QoS flow and can have multiple non-default QoS flows.
D. A PDU session has one or more UPFs acting as PDU session anchors.
Which of the following actions is NOT performed when handling an uplink data packet?
A. UE maps the uplink data packet to a QoS Flow based on QoS rules received from SMF.
B. UE maps the QoS Flow identifier to a data radio bearer based on QFI-to-DRB mapping received from NG-RAN.
C. NG-RAN marks the data packet with the proper DSCP value.
D. NG-RAN removes the QoS Flow identifier from the packet header and forwards the packet over the proper N3 GTP-U tunnel.