4A0-106 Online Practice Questions and Answers
In a VPRN, which of the following are supported as PE-CE routing methods on the Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR? (Choose four).
A. Static
B. RIP
C. OSPF
D. IS-IS
E. MP-BGP
F. BGP
An advantage of using BGP as the PE-CE protocol is that route policies are no longer required to control the exchange of routes from BGP to MP-BGP.
A. True
B. False
Which of the following about eiBGP Load Balancing is FALSE?
A. ecmp and multipath must be configured within the VPRN instance.
B. The RD of the VPRN on the local PE must be different from the RD of the remote PEs.
C. Is enabled in the config>router>bgp context
D. Allows a PE router to load share traffic across routes learned from both direct CE-PE peerings and MPBGP peerings.
Which of the following VPRN label allocation methods are supported by the Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR?
A. One label per VRF per route
B. One label per VRF per next-hop
C. One label per VRF
D. All of the above
E. A and C
F. B and C
Click the exhibit.
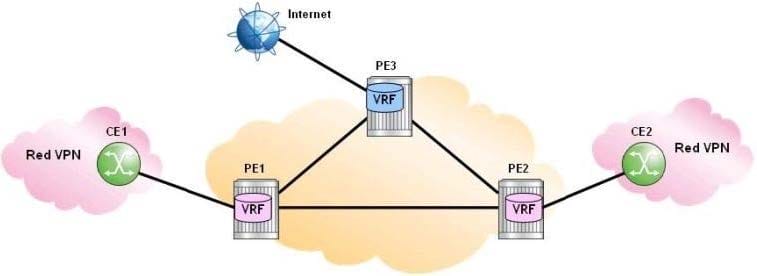
PE3 learns Internet routes via its VRF interface to the Internet peering router and stores them in its Internet VRF. CE1 is connected to the Red VPN and requires Internet access via its Red VRF interface. Which of the following statements do not fulfill this requirement?
A. PE1 advertises the Red VPN routes and a default route to PE3.
B. The Internet VRF on PE3 imports the Red VPN routes advertised by PE1.
C. PE1 imports all Internet routes and advertises them to CE1 via the Red VRF.
D. PE3 advertises a default route from its Internet VRF instead of advertising all Internet routes.
On a PE router, the VRF table for VPRN 10 contains: one local route, two BGP routes learned from a local CE, and three tunneled routes learned from a remote site. If we execute the command "configure service vprn 10 maximum-routes 2 log-only" on this PE router, how many routes are expected to be in the VRF?
A. Five routes: the local route, the two BGP routes learned from the local CE, and two tunneled routes.
B. Six routes: the local route, the two BGP routes learned from the local CE, and three tunneled routes.
C. Two routes: the local route and one tunneled route.
D. Three routes: the local route and two tunneled routes.
E. Two routes: the local route and one BGP route learned from the local CE.
Click the exhibit.
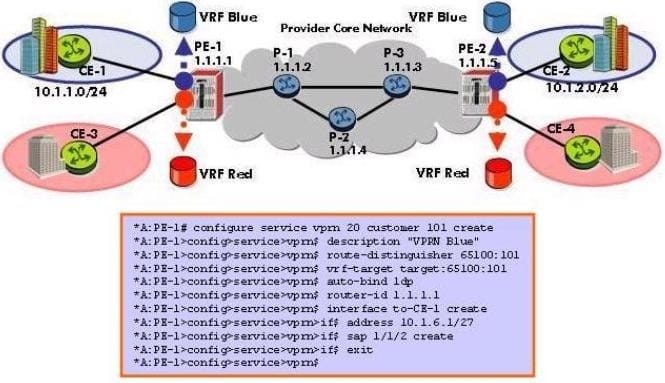
What is wrong with the VPRN configuration applied on this Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR?
A. The VPRN ID must match the value used in the vrf-target command.
B. The VPRN ID must match the value used in the route-distinguisher command.
C. The router-id command should not be used in this context.
D. The "no shutdown" command must be configured for the VPRN to be operationally UP.
Click the exhibit.
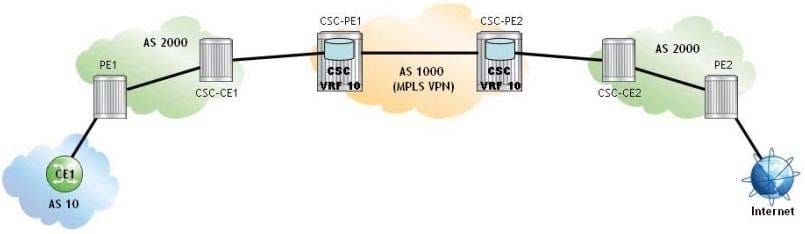
A Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) VPRN is configured for a customer carrier who is an Internet Service Provider (ISP). Which of the following about route distribution is FALSE?
A. The VRF 10 on CSC-PE1 includes PE1 and PE2's system addresses.
B. The global routing table of PE1 includes PE2's system address.
C. The VRF 10 on CSC-PE2 includes CEI'S address.
D. The global routing table of PE2 includes CE1's address.
Click the exhibit.
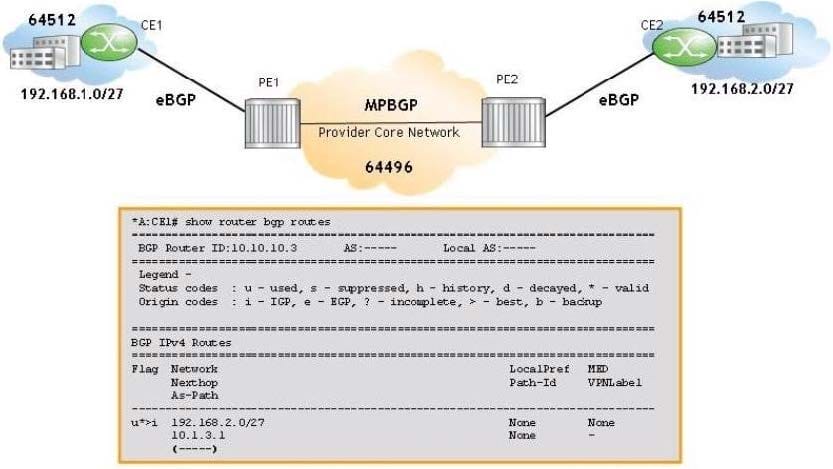
The CLI command "remove-private" is configured on PE1 to eliminate BGP loops in the VPRN. For the displayed route, what is the value of the AS-Path field?
A. 64496 64512
B. 64512
C. 64496
D. 64512 64496
For the Inter-AS model A VPRN, which of the following is FALSE when CE2 sends an IP packet to 192.168.1.1?
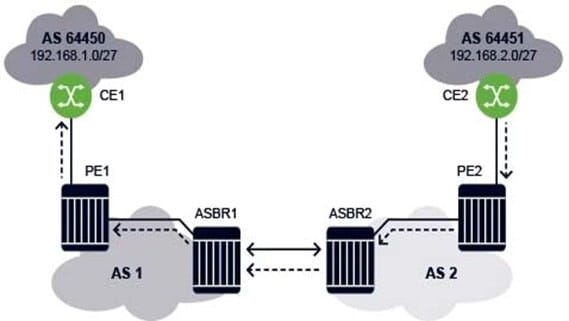
A. CE2 forwards an unlabeled IP packet to PE2 via the VPRN interface.
B. PE2 pushes one label on the IP packet and label-switches it to ASBR2.
C. ASBR2 forwards an unlabeled IP packet to ASBR1.
D. ASBR1 pushes two labels on the IP packet and label-switches the packet to PE1.