352-001 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Which three statements about EIGRP route summarization are correct? (Choose three.)
A. By default, all EIGRP routes are automatically summarized; all routes will be summarized unless the noauto summary command is configured.
B. By default, EIGRP automatically summarizes internal routes, but only each time a major network boundary is crossed.
C. EIGRP route summarization can reduce the query diameter to help prevent SIA problems.
D. Summary routes are inserted in the routing table with a next hop of null 0 and a high administrative distance, to prevent black holing of traffic.
E. The metric for each summarized route is inherited from the lowest metric of the component routes.
Which statement is true about connecting an IP multicast domain that is operating in PIM dense mode to a PIM sparse mode domain?
A. The interconnection must be made at the rendezvous point of the PIM sparse mode domain.
B. The connection can be made at any location in the network, as PIM sparse mode will inter-operate seamlessly with PIM dense mode.
C. PIM dense mode and sparse mode domains are not inter-operable and cannot be connected.
D. The connection can be made at any location in the network, but PIM sparse mode and PIM dense mode cannot inter-operate; IGMP must be used to provide the interconnection.
Which of these is an advantage of creating an in-band rather than an out-of-band management network?
A. protection of management traffic
B. lower equipment costs
C. separate transport equipment
D. protection of production traffic
Which two resources are propagated by the headend router for constrained based path computation with MPLS Traffic Engineering? (Choose two.)
A. average link utilization
B. average input queue depth
C. link bandwidth
D. link affinity
E. link delay
F. link jitter
Which three factors slow down network convergence? (Choose three.)
A. constant interface flapping
B. lack of redundant paths
C. inconsistent topology states between routers
D. transport network failing to generate LoS
E. wrong summarization in ABRs
Refer to the exhibit.
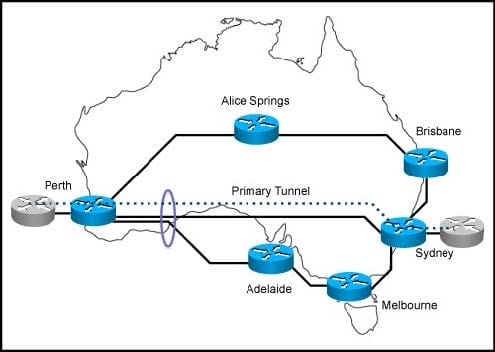
You are designing MPLS-TE for this network. The links from Perth to Sydney and from Perth to Adelaide share the same optical fiber in one given segment. Which feature should you implement to eliminate the risk that a backup tunnel is installed over the same optical fiber as the primary one?
A. DiffServ Traffic Engineering
B. Forwarding Adjacency
C. MPLS-TE Path Protection
D. Shared Risk Link Groups
E. MPLS-TE Link Protection
Which two steps can be taken by the sinkhole technique? (Choose two.)
A. Delay an attack from reaching its target
B. Redirect an attack away from its target
C. Monitor attack noise, scans, and other activity
D. Reverse the direction of an attack
Which MPLS attribute is required for links to carry a given MPLSTE tunnel?
A. TE tunnel destination address
B. Tunnel path-selection metric
C. Affinity
D. Next-hop backup tunnel
As network designer, which option is your main concern with regards to virtualizing multiple network zones into a single hardware device?
A. Fate sharing
B. CPU resource allocation
C. Congestion control
D. Security
E. Bandwidth allocation
A network designer decides to connect two labs together to test multicast features interoperability. Before the networks are connected together, the network administrator mentions that overlapping multicast IP addresses between the two labs will cause issues because all the routers on the network are provisioned for Source-Specific Multicast using IGMPv3.
Which statement about the connectivity of both multicast domains is true?
A. IGMPv3 can support overlapping multicast IP addresses between the labs
B. IGMPv3 cannot support overlapping multicast IP addresses between the labs
C. IGMPv3 requires NAT to support the overlapping multicast IP addresses between the labs
D. IGMPv3 requires a unique RP when connecting both labs together